Linear Simulation (LSIM)
Features and Benefits
- Linear signal modeling from digital input to acoustical output
- Lumped network parameters for passive components
- Automatic equalization (DSP)
- Small signal performance for any audio input (music, test signal)
- Efficiency and voltage sensitivity versus frequency and broadband signals
- Acoustical parameters from geometrical input
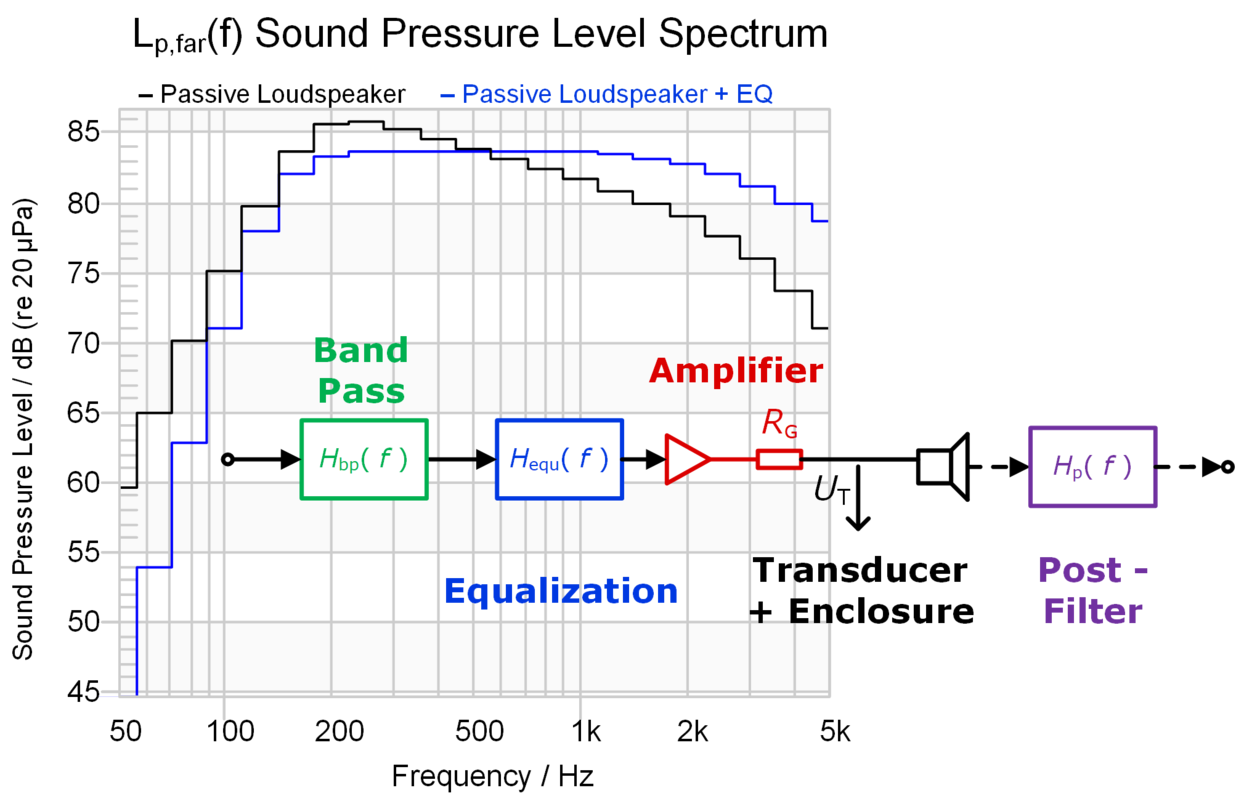
The LSIM Linear Simulation describes an active loudspeaker or headphone driver by using a linear lumped parameter model. The main components are equalizer, amplifier, transducer and enclosure. Using any selected input spectrum (e.g. music), meaningful statistical single values (e.g. mean efficiency) and various state spectra (e.g. SPL) are calculated. This is a useful base for defining transducer and amplifier requirements and providing significant information about the audio performance. Various transfer functions reveal the relationship between digital, electrical, mechanical and acoustical signals.
The LSIM features an easy-to-use simulation software with lumped or geometrical input parameters for initial (small signal) design, which is the basis for the large signal simulation in other Klippel software modules (SIM Simulation, SIM AUR Auralization).
Specification
Demo Video
What's New in dB-Lab 212: Linear Simulation (LSIM)
With loading this video, you agree that your data will be transferred to YouTube and that you have read our data protection policy.
Requirements
Literature and Papers
Standards
International Electrotechnical Commission
IEC 60268-5, IEC 60268-7, IEC 60268-21, IEC 60268-22, IEC 62458, IEC WD 63034
European Standards
BS EN 54-24, BS EN 50332
Audio Engineering Society
AES2, AES56